Introduction to PyTorch
Background
PyTorch is a widely used deep learning platform known for its flexibility and speed. Originally developed by Facebook AI (now Meta AI), it has grown into one of the most popular frameworks for deep learning research and applications. Researchers and industry professionals widely adopt it due to its ease of use, dynamic computation graph, and easy integration with GPU acceleration.
PyTorch evolved from the Torch library, which was an open-source deep learning framework written in C. Although Torch is no longer actively developed, many of its libraries and functionalities have been incorporated into PyTorch. Today, PyTorch is used by corporations, laboratories, and universities to develop software like Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) models (Tesla), ChatGPT (OpenAI), reinforcement learning models for robotics (Boston Dynamics), and much more.
Overview of PyTorch and Its Core Components
PyTorch provides a comprehensive set of tools and features that enable efficient deep learning model development and training. Below are some of its core components:
1. Torch Tensors
A tensor is a multi-dimensional array, similar to NumPy arrays, but with the added benefit of GPU acceleration and automatic differentiation.Tensors are the core data structure in PyTorch, used to store and manipulate data for deep learning models. Every input in PyTorch is represented as a tensor; features, responses, parameters, etc. PyTorch does not accept numpy arrays as input like Keras/TensorFlow does, but numpy arrays are easily converted to and from Torch tensors.
Creating Tensors
import torch
# Creating a tensor from a list
x = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], dtype = torch.float)
# Creating a random tensor
rand_tensor = torch.rand(3, 3) # 3x3 matrix
# Creating a tensor filled with zeros or ones
zero_tensor = torch.zeros(5, 5) # 5x5 matirx
one_tensor = torch.ones(5,5) # 5x5 matirx
# Make a row tensor a column tensor
column = torch.tensor([1,2,3,4,5]).view(-1,1)
# Convert a Numpy array to a tensor
array = np.array([1,2,3,4])
tensor = torch.tensor(array)
# or
tensor = torch.from_numpy(array)
# Convert back to array
array = tensor.numpy()
Tensor Operations
x = torch.tensor([2,4,6])
y = torch.tensor([1,3,5])
# Matrix Addition
z = x + y
z = x * y
# Matrix Multiplication
z = torch.matmul(x, torch.t(y))
Automatic Differentiation
Automatic differentiation (autograd) is a technique used by PyTorch to compute derivatives (gradients) automatically, making it easier to train deep learning models. It dynamically builds a computational graph and efficiently applies the chain rule for differentiation.
# Create tensor with gradient tracking
x = torch.tensor(2.0, requires_grad=True)
If a tensor has requires_grad = True, PyTorch keeps track of all operations performed on it.
Computing Gradients
When .backward() is called on a scalar loss, PyTorch traverses the graph in reverse (backpropagation) and computes derivatives using the chain rule. The computed gradients are stored in the .grad attribute of each tensor. The gradients are then used to update model parameters (e.g., via gradient descent). We’ll talk more about backpropogation on the next page.
Key Features of Autograd
- Dynamic Computation Graph: Built at runtime, allowing flexibility in model design.
- Efficient Backpropagation: Computes gradients only for required tensors.
- Automatic Chain Rule Application: Saves time and avoids manual derivative computation.
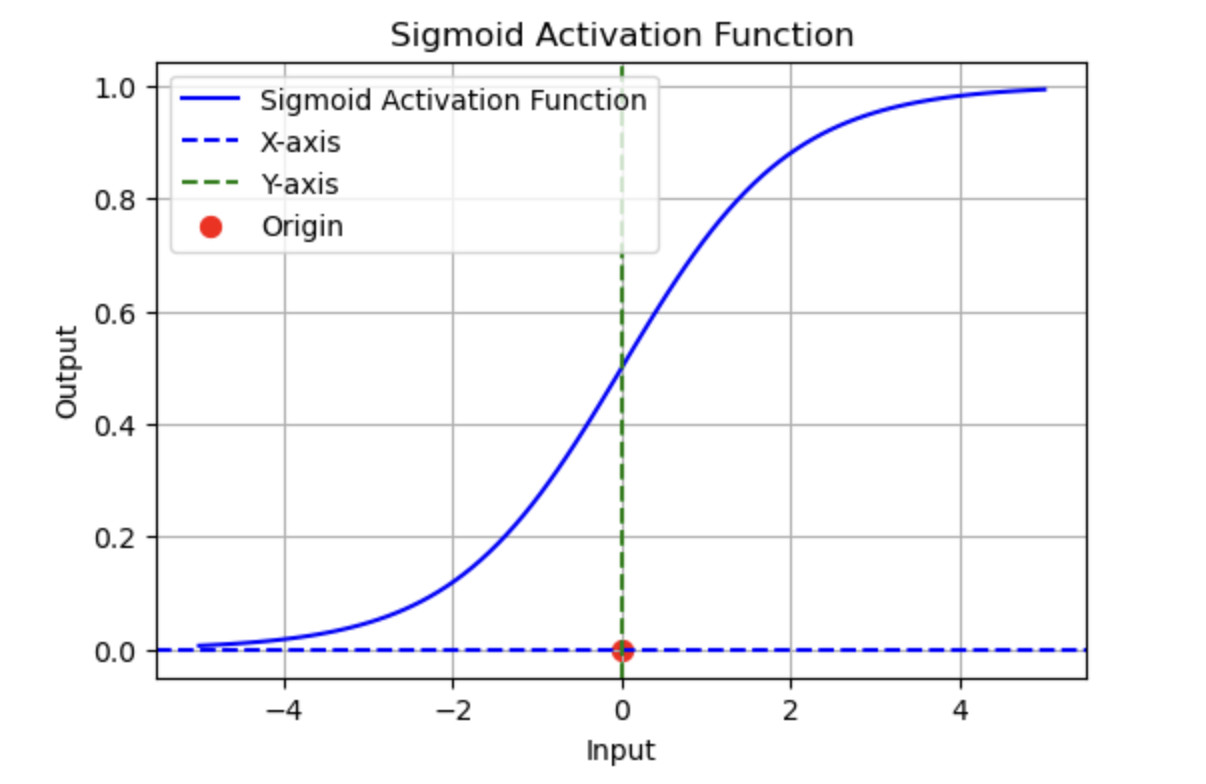
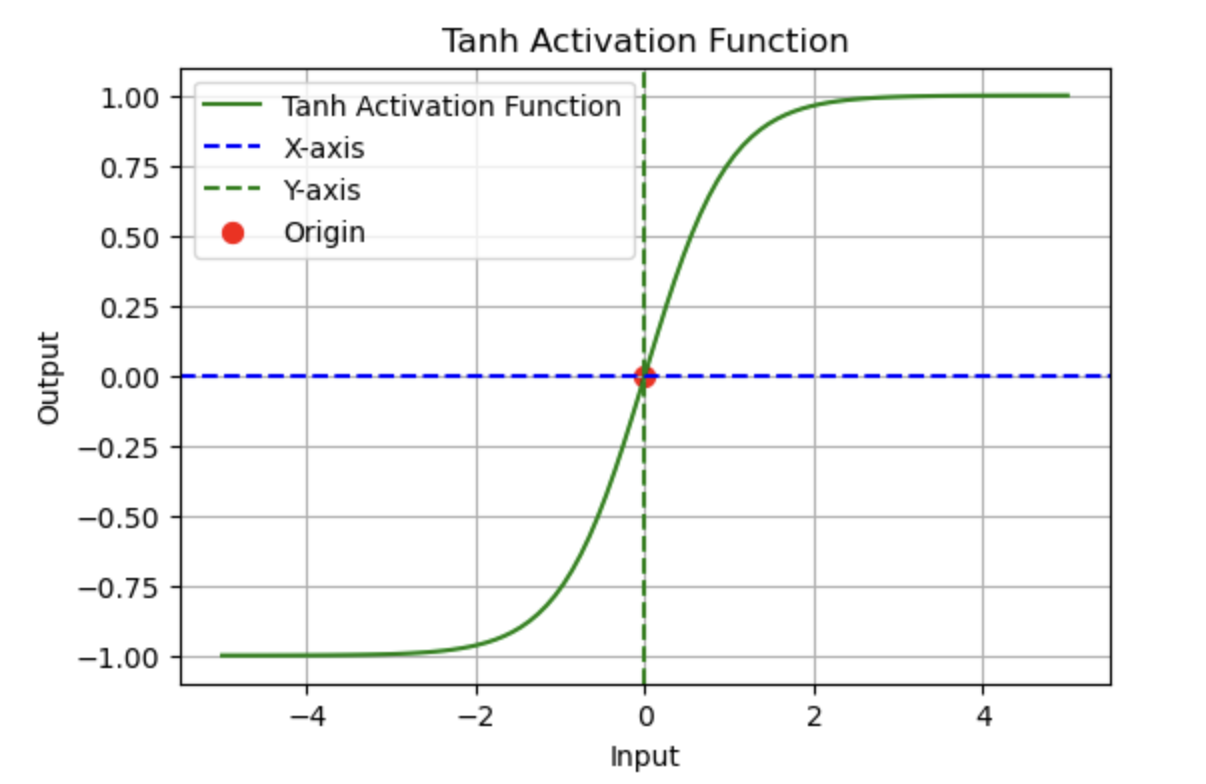
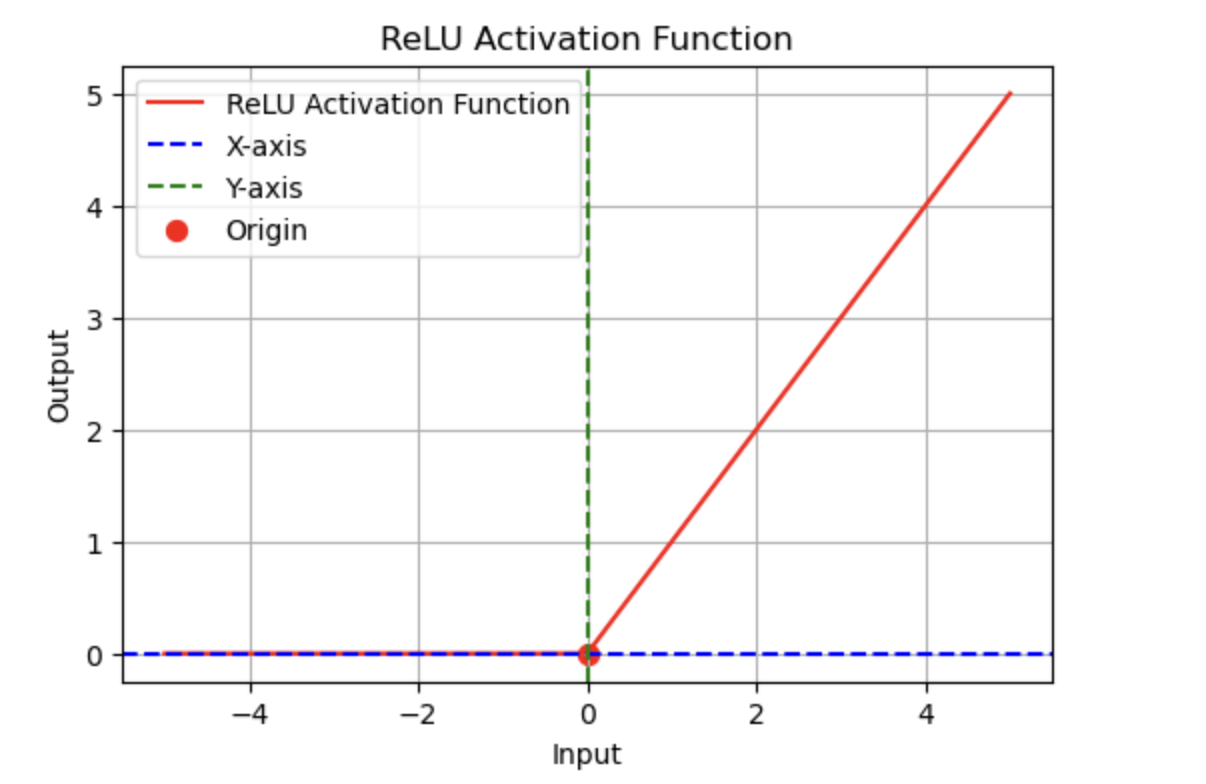
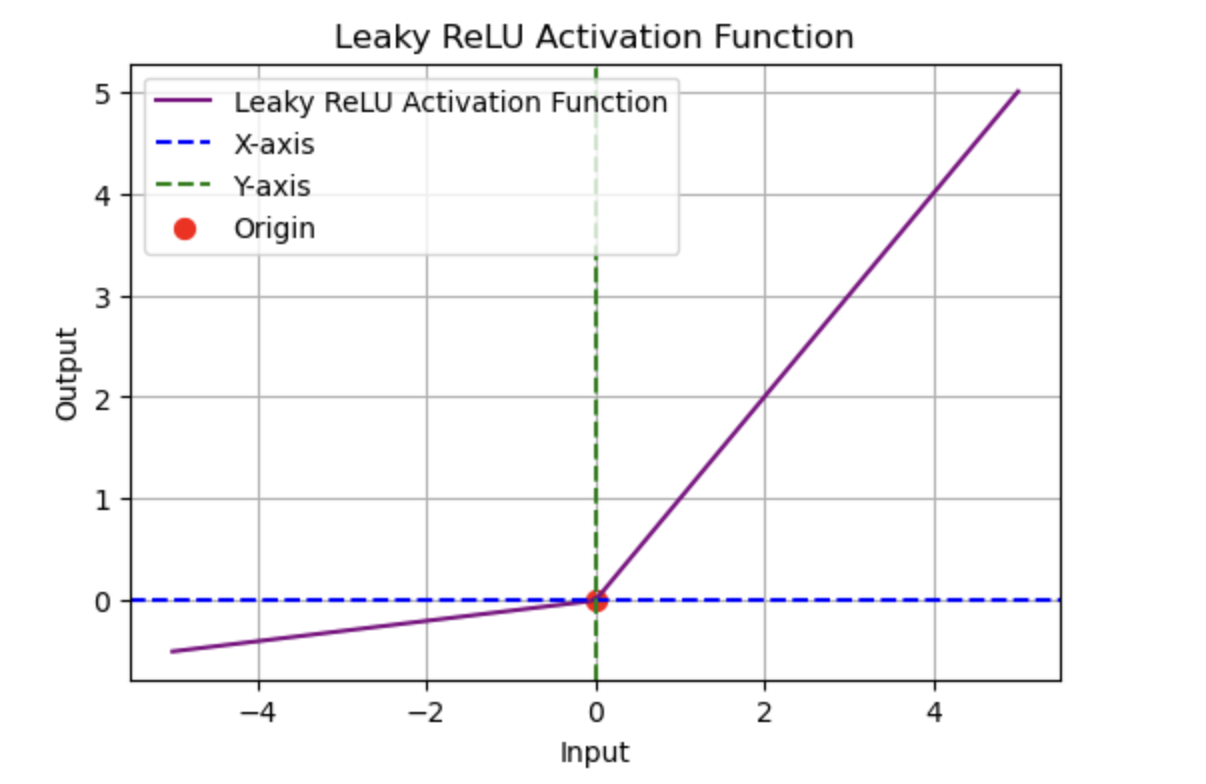
2. Activation Functions
Activation functions introduce non-linearity into neural networks, enabling them to learn and model complex patterns.
Common Activation Functions in PyTorch
import torch.nn as nn
# Sigmoid Activation
sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
# ReLU Activation
relu = nn.ReLU()
# Tanh Activation
tanh = nn.Tanh()
# Leaky ReLU
lrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01)
More Activation Functions
3. Loss Functions
A loss function measures how well or poorly a model performs by comparing the model’s output to the true labels
Common Loss Functions
mse_loss = nn.MSELoss() # Mean Squared Error
ce_loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # Cross-Entropy Loss
bce_loss = nn.BCELoss() # Binary Cross-Entropy Loss
nll_loss = nn.NLLLoss() # Negative Log-Likelihood (NLL) Loss
hu_loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss() # Huber Loss (Smooth L1 Loss):
More Loss Functions
4. Optimizers
Optimizers are algorithms used to update the weights of a neural network during training to minimize the loss function. They adjust model parameters based on gradients computed during backpropagation to improve the model’s performance.
Common PyTorch Optimizers
import torch.optim as optim
# Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
sgd = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# Adam Optimizer
adam = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# RMSprop: (Root Mean Square Propagation):
rmsprop = optim.RMSprop(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# Adagrad:
adagrad = optim.Adagrad(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
The model parameters are passed through the optimizer. This is essential for training.
More Optimizers
5. Transforms
PyTorch Transforms are operations used to preprocess and augment data before feeding it into a neural network. They are commonly used in computer vision tasks to prepare images for training. Other data types have other augmenters.
Example Image Transformations
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((128, 128)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.5], std=[0.5])
])
More Transforms
6. Data Handling with Dataset and DataLoader
PyTorch provides powerful tools for handling datasets efficiently using torch.utils.data.Dataset and torch.utils.data.DataLoader. These utilities make it easy to preprocess and load data in batches, which is essential for training deep learning models effectively.
Using Dataset to Create Custom Datasets
torch.utils.data.Dataset is an abstract class representing a dataset. PyTorch Datasets provide an easy way to load, preprocess, iterate through, and manage data in PyTorch.Your custom dataset should inherit Dataset and override the following methods:
- init: point to your own dataset
- len : ensure len(dataset) returns the correct length of the dataset.
- getitem: to iterate through data
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data, labels):
self.data = data
self.labels = labels
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.data[idx], self.labels[idx]
Using DataLoader to Load Data Efficiently
The DataLoader class provides an efficient way to load and iterate through the dataset in mini-batches, enabling better performance and faster training.
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataloader = DataLoader(CustomDataset(data, labels), batch_size=32, shuffle=True)
# Example: Iterating through batches
for batch in dataloader:
inputs, targets = batch
print(inputs.shape, targets.shape)
Key Features of DataLoader
- Batching: Automatically divides data into batches to optimize training.
- Shuffling: Randomly shuffles data at each epoch to improve model generalization.
- Parallel Processing: Uses multiple workers to speed up data loading.
- Pin Memory: Optimizes memory transfer between CPU and GPU for better performance.
Using Dataset and DataLoader correctly can significantly enhance the efficiency of deep learning pipelines, making it easier to work with large-scale datasets.
Advantages of PyTorch
PyTorch is a widely used deep learning framework known for its flexibility, ease of use, and strong ecosystem. Key advantages include:
-
Dynamic Computation Graphs (Define-by-Run) Unlike TensorFlow’s older static graphs, PyTorch builds computation graphs dynamically, enabling intuitive debugging, flexible model modifications, and support for variable-length inputs—essential for NLP and reinforcement learning. Learn more about dynamic computation.
-
Seamless GPU Acceleration PyTorch easily utilizes GPUs with .to(device), supports mixed precision training (torch.cuda.amp), and scales efficiently with DataParallel and DistributedDataParallel for multi-GPU training.
-
Integration with the Python Ecosystem PyTorch works seamlessly with NumPy, SciPy, and Pandas, allowing easy data preprocessing and interoperability with scikit-learn, TensorBoard, and wandb.
-
Strong Community & Ecosystem With extensive documentation, active forums, and widespread industry adoption, PyTorch benefits from constant improvements and extensive open-source contributions.
-
Excellent Support for Computer Vision & NLP With TorchVision, TorchText, and TorchAudio, PyTorch simplifies deep learning applications in vision, language processing, and audio analysis.